A collaborative team from Promation, ModuleWorks, and Multi-Scale Additive Manufacturing (MSAM) Laboratory of the University of Waterloo has developed and successfully tested a new method for manufacturing overhang geometries without the need for support structures. The tests were conducted at the University of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada using Laser Directed Energy Deposition (LDED). By eliminating support structures, the team was able to simplify process planning and reduce waste material.
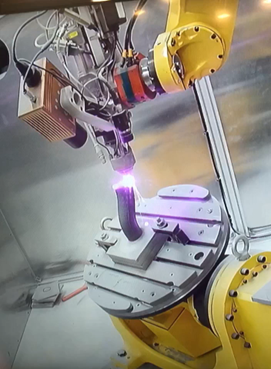
Laser Directed Energy Deposition of a pipe without support structures using a Fanuc 6-axis robot. Image courtesy of MSAM of the University of Waterloo.
Parts with geometric overhangs, such as pipes with bends, pose a special challenge for additive processes that deposit material in horizontal layers. To deposit material in the overhang area of the bend, the process needs to incorporate support structures that allow the layers to extend beyond the pipe. This works well enough but incorporating support structures adds time and effort to production planning and creates extra waste material.
To simplify and speed up the LDED process, Promation, ModuleWorks, and MSAM teamed up to develop a new method that deposits the layers in non-horizontal planes. The printing nozzle is mounted on a 6-axis robotic arm to ensure it always remains tangent to the deposition surface which is automatically tilted using a 2-axis positioner. Applying deposition layers to a tilted surface enables pipe bends and other overhang geometries to be printed without support structures, which simplifies production planning and reduces waste material.
In the laboratory tests, the team used the new method to manufacture a pipe with a 45-degree bend with no support structures. The new method was also used to successfully print a closed hollow dome.
Laser Directed Energy Deposition of closed hollow dome without support structures using a Fanuc 6-axis robot. Image courtesy of MSAM of the University of Waterloo.
About ModuleWorks
ModuleWorks is the leading software component provider for the digital manufacturing industry. With over 200 employees and 1300 person-years of software development, ModuleWorks’ expertise in toolpath creation and simulation is recognized throughout the industry and its software components are already optimizing the performance and quality of over 500,000 installed seats of CAD/CAM and CNC software around the world.
From standard products to exclusive development projects, ModuleWorks helps companies to bring their vision of Industry 4.0 to life. With its comprehensive portfolio of cutting-edge software components, ModuleWorks enables its customers to optimize their CAD/CAM solutions and connect to CNC/MTB systems to increase their competitiveness and help them Get There Faster.
About Promation
Promation is a leading designer and manufacturer of high-quality tooling, automation, and robotic systems. With a strong commitment to excellence and strict conformance to quality management programs, Promation employs nimble and effective Project Management, Engineering, Quality Assurance, and Manufacturing expertise to successfully deliver custom equipment and engineered turnkey systems on time and on budget, while catering to the unique quality and safety requirements of the nuclear industry.
Promation collaborated with MSAM of the University of Waterloo to develop a new generation of robotics LDED-PF systems. Promation research covers the entire development of the AM system with embedded in-situ quality assurance techniques to accelerate the industrialization of AM technologies.
Our organization embodies its commitment to embracing ethnic, gender and cultural diversity within its business practices and is proud to be an inclusive, socially responsible corporation. Discover more at www.promation.com or on our LinkedIn page.
About Multi-Scale Additive Manufacturing Lab (MSAM) of the University of Waterloo
The MSAM Lab, located at the Department of Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering of the University of Waterloo in Canada, focuses on next-generation additive manufacturing processes. To this end, the lab explores novel techniques to develop advanced materials, innovative products, modeling and simulation tools, monitoring devices, closed-loop control systems, quality assurance algorithms and holistic in-situ and ex-situ characterization techniques.
MSAM’s research covers the entire development cycle of an additively manufactured product, ranging from material characterization, and improvement to an existing machine or new process development under eight research themes. We are also working closely with our industrial partners in determining the best technology and process parameters to utilize in creating their specific parts using additive manufacturing.